Have you ever noticed condensation dripping from your metal roof panels during temperature changes, or experienced unexplained energy bills that seem to climb despite your best efforts? These frustrating scenarios often stem from one overlooked detail: improper air gap design in Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems. Understanding air gap requirements is not just a technical specification—it's the critical difference between a roofing system that performs optimally for decades and one that fails prematurely, costing you thousands in repairs and energy waste. This comprehensive guide reveals how proper ventilation channels protect your investment, regulate thermal performance, and ensure your metal roofing delivers the long-term durability you expect.

The Science Behind Air Gaps in Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems
Air gaps represent engineered ventilation channels strategically positioned between metal roofing panels and the underlying roof deck or insulation layer. In Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems, these carefully calculated spaces serve multiple critical functions that directly impact both the immediate performance and long-term durability of your entire roofing assembly. The fundamental principle revolves around thermodynamic management and moisture control through continuous airflow pathways that extend from intake points at the eaves to exhaust locations at the ridge or gable ends. When metal panels are exposed to direct solar radiation, surface temperatures can reach levels significantly higher than ambient air temperature—sometimes exceeding 150°F in peak summer conditions. Without adequate air gap design, this thermal energy transfers directly through the roof assembly, dramatically increasing cooling loads and creating temperature differentials that promote condensation formation. The air gap functions as a thermal break, allowing convective cooling to dissipate accumulated heat before it penetrates into the building envelope. This principle becomes especially critical in Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems where the continuous panel design and mechanical seaming create highly conductive pathways for thermal energy transfer.
-
Moisture Management Through Ventilation Channels
The relationship between air gaps and moisture control represents perhaps the most critical aspect of metal roof performance. During nighttime hours, metal roofing surfaces can radiate heat to the clear sky, causing panel temperatures to drop below ambient air temperature—sometimes by 18°F or more in optimal conditions. This phenomenon, known as radiative cooling, creates ideal conditions for condensation when warm, moisture-laden air contacts the cold metal surface. Properly designed air gaps in Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems create ventilation pathways that continuously evacuate humid air before condensation occurs, maintaining dry conditions throughout the assembly. Research conducted at Oak Ridge National Laboratory has demonstrated that ventilated metal roofing systems significantly outperform non-ventilated assemblies in managing diurnal temperature fluctuations and reducing heat flow through the roof structure. The studies compared various ventilation configurations against control assemblies without air gaps, measuring temperature differentials, moisture accumulation, and energy transfer rates. Results consistently showed that air gap depths of 0.75 inches to 4 inches provided measurable benefits in thermal performance and condensation prevention, with optimal performance occurring in the 1-inch to 2-inch range for most climatic conditions.
Optimal Air Gap Dimensions for Standing Seam Metal Roof Applications
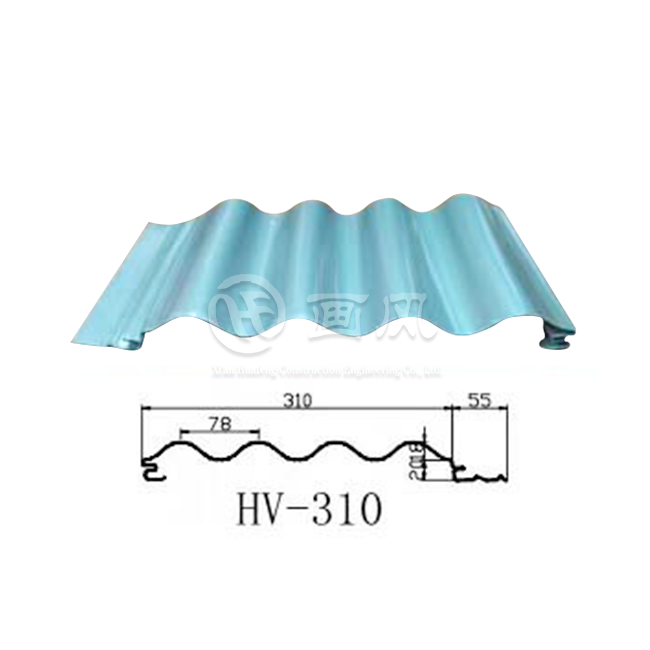
Determining the appropriate air gap dimension for Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems requires careful consideration of multiple factors including climate zone, roof pitch, building use, and specific performance objectives. Industry research and field experience have established general guidelines that serve as starting points for system design, though project-specific engineering analysis should always inform final specifications. The minimum effective air gap typically ranges from 0.75 inches to 1 inch, providing basic ventilation and thermal break functionality suitable for moderate climates with minimal extreme temperature or humidity challenges. For enhanced performance in demanding applications, air gap dimensions between 1.5 inches and 4 inches deliver superior results. Hot climate installations benefit significantly from larger air gaps approaching the 3-inch to 4-inch range, where increased airflow volume provides greater convective cooling capacity. This enhanced ventilation reduces metal panel operating temperatures by 15°F to 25°F compared to direct-applied installations, substantially lowering heat transfer into conditioned spaces and reducing cooling energy consumption by measurable percentages. Cold climate applications similarly benefit from robust air gap design, though the primary objective shifts toward moisture management and ice dam prevention rather than thermal load reduction.
-
Installation Methods and Material Considerations
Creating consistent, reliable air gaps in Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems requires appropriate installation techniques and carefully selected materials. Three primary approaches dominate current industry practice, each offering distinct advantages for specific applications. Traditional wood furring strips or battens—typically 1x3 or 1x4 dimensional lumber—provide proven performance when installed either perpendicular to panel direction for structural support or diagonally for combined support and drainage pathways. The diagonal installation method, often specified at 45-degree angles with strategic gaps between batten runs, creates both effective ventilation channels and drainage paths for any water that might penetrate the roofing system. Advanced alternatives to traditional battens include three-dimensional mesh products and ventilated dimple mats that offer different installation characteristics and performance profiles. The 3D mesh systems typically provide air gaps in the 0.25-inch to 0.5-inch range through polymer fiber matrices that allow both horizontal and vertical airflow while providing minimal drainage capacity. These products excel in renovation applications where structural capacity limits additional dead loads or where minimal profile increase is desired. Ventilated dimple mats create slightly larger air gaps through embossed patterns in sheet materials, combining drainage functionality with ventilation performance in a single-component system that simplifies installation compared to traditional batten approaches.
When specifying materials for air gap creation in Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems, several critical factors demand attention. Wood battens must be pressure-treated or naturally durable species to resist moisture-related degradation within the ventilation cavity. Fastener selection requires particular care, as attachment points must penetrate through air gap materials and underlayment into structural decking with sufficient embedment to resist wind uplift forces transmitted through the roofing panels and clips. Engineering analysis should verify that fastener schedules and batten spacing provide adequate support for the standing seam panel profile being installed, considering both panel gauge and expected loads from snow accumulation, wind events, and maintenance access.
Climate-Specific Requirements for Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems
Regional climate conditions fundamentally shape air gap requirements and optimal design approaches for Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems. Hot, arid climates present challenges primarily related to extreme solar heat gain and high thermal cycling that expands and contracts metal panels through their full dimensional range daily. In these environments, air gap dimensions at the upper end of the recommended spectrum—approaching 3 inches to 4 inches—deliver optimal performance by maximizing convective cooling potential. Light-colored or reflective metal finishes amplify this benefit, with PVDF coatings in reflective tones reducing solar heat absorption by 30% to 40% compared to darker colors, while the air gap evacuates residual thermal energy before it penetrates the building envelope. Hot, humid coastal regions compound solar heat gain challenges with elevated atmospheric moisture content and salt-laden air that accelerates corrosion of inadequately protected components. These demanding environments require both robust air gap ventilation and corrosion-resistant material selections throughout the assembly. Stainless steel fasteners become essential rather than optional, while aluminum or stainless steel standing seam panels provide superior longevity compared to galvanized or galvalume options in direct salt exposure. The air gap design must emphasize moisture evacuation through continuous soffit-to-ridge ventilation pathways that prevent humid air stagnation within the cavity, where persistent moisture exposure would accelerate corrosion of structural components and fasteners.
-
Cold Climate and Ice Dam Prevention
Cold climate installations present distinctly different priorities where air gap design directly impacts ice dam formation and winter performance characteristics. When interior heat escapes through ceiling assemblies into ventilated attic spaces, it can warm roof surfaces unevenly, melting snow in mid-roof areas while eaves remain frozen. This meltwater runs down-slope until reaching the cold eave zone, where it refreezes and gradually builds ice dams that block subsequent drainage and force water infiltration under roofing materials. Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems with properly designed air gaps break this destructive cycle by maintaining uniform cold roof surface temperatures that prevent differential melting and ice dam initiation. The critical factor in cold climate air gap design involves ensuring continuous ventilation from eave intake points to ridge exhaust locations without interruption or restriction. Even small breaks in the ventilation pathway can create warm zones where snow melting initiates. Many designers specify air gap depths of 1.5 inches to 2 inches for cold climate applications, providing robust airflow capacity that maintains consistent roof surface temperatures even when substantial interior heat loss occurs through ceiling assemblies. This approach proves particularly essential for cathedral ceiling applications where interior finish surfaces contact roof decking with only insulation separation, as these assemblies lack the thermal buffering effect of traditional attic spaces.
Integration with Complete Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems
Effective air gap design cannot be considered in isolation but must integrate seamlessly with all other components of Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems to deliver optimal performance. The relationship between air gaps and waterproof membranes exemplifies this integration requirement. High-temperature synthetic underlayments provide essential secondary weather protection while withstanding the elevated temperatures that occur in ventilated metal roofing assemblies. These specialized membranes resist degradation at operating temperatures that would compromise traditional felt products, maintaining waterproofing integrity throughout the 30-year-plus service life expected from quality metal roofing installations. The standing seam panel profile itself influences air gap requirements through its unique structural and thermal characteristics. Panels with 65mm seam heights, such as those manufactured by Xi'an Huafeng Construction Engineering Co., Ltd., provide exceptional structural rigidity and weather resistance through their elevated profile design. This increased panel depth creates additional thermal mass that can amplify temperature-related performance challenges when installed without adequate ventilation, making proper air gap design even more critical for tall-seam profiles. The mechanical seaming method used to join adjacent panels creates continuous, raised ribs that enhance structural performance while also providing natural drainage channels that complement the air gap ventilation strategy.
-
Insulation Coordination and Thermal Performance
The thermal insulation strategy employed within the roof assembly dramatically affects air gap requirements and overall system performance. Traditional vented attic assemblies with ceiling-level insulation rely on attic ventilation as the primary moisture management mechanism, with the metal roof air gap serving primarily to reduce panel operating temperatures and extend service life through thermal load reduction. These assemblies prove most tolerant of air gap design variations, as the substantial air volume in the attic space provides thermal buffering that moderates condensation risk even if metal roof ventilation proves marginal. Unvented conditioned attic assemblies or cathedral ceiling applications eliminate the attic buffer, placing complete reliance on the air gap ventilation system for moisture management and thermal control. These demanding applications require more rigorous air gap design with particular attention to intake and exhaust vent sizing, pathway continuity, and coordination with vapor barrier placement. Above-sheathing insulation approaches, where rigid foam boards are installed over structural decking before Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems installation, create especially sensitive conditions that mandate robust air gap ventilation. The continuous insulation layer eliminates any drying potential toward the interior, making the air gap the sole moisture evacuation pathway for any vapor that migrates through the assembly. Minimum air gap dimensions for these applications should not fall below 1 inch, with 1.5-inch to 2-inch gaps providing greater reliability and margin for climate variation.
Professional Design and Implementation Best Practices
Translating air gap theory into successful field installations requires attention to numerous practical details that separate optimal performance from marginally adequate systems. The intake and exhaust vent sizing calculation represents a fundamental starting point that many projects inadequately address. Building codes typically specify minimum net free vent area requirements based on attic floor area, with standard ratios of 1 square foot of vent area per 150 square feet of attic space when intake and exhaust vents are balanced, or 1:300 when ventilation is provided by exhaust vents alone. These minimum code requirements, however, often prove insufficient for Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems where enhanced ventilation delivers measurable performance benefits. Best practice approaches calculate vent area requirements based on air gap volume and desired air change rates rather than relying solely on code minimums. Industry guidelines suggest targeting air change rates of 10 to 15 per hour within the ventilation cavity for optimal moisture removal and thermal management. For a typical residential roof with 2,000 square feet of surface area and a 2-inch air gap, this translates to ventilation cavity volume of approximately 333 cubic feet. Achieving 10 air changes per hour requires moving 3,330 cubic feet per hour, or approximately 55 cubic feet per minute of airflow through the cavity. This airflow rate can be achieved through properly sized continuous soffit and ridge vents that leverage natural convective stack effect without requiring mechanical ventilation assistance.
-
Installation Details and Quality Control
Field installation quality determines whether carefully engineered air gap designs deliver their theoretical benefits or fail to meet performance expectations. Several critical details demand rigorous attention during construction to ensure successful outcomes. Batten or spacer installation must maintain consistent dimensions and spacing throughout the roof surface, as variations create areas of restricted airflow that compromise overall system performance. When using wood battens, attachment fastener patterns must provide secure anchorage without creating thermal bridges that conduct heat or cold through the assembly. Diagonal batten installations require particular care to maintain proper end gaps that allow air and water movement between adjacent batten runs while still providing continuous support for roofing panel clip attachment.
Edge closures at eaves and rakes present challenging details where air gap ventilation requirements conflict with weatherproofing and pest exclusion objectives. Solid closure strips that block the air gap completely defeat the ventilation system, yet open gaps invite insect intrusion and weather infiltration. Purpose-designed vent closure strips that incorporate screened openings resolve this conflict by maintaining airflow pathways while excluding pests and weather. These specialized products come in profiles matched to specific Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems panel configurations, ensuring proper fit and weather performance. Ridge vent installations similarly require careful product selection and installation technique to provide adequate exhaust capacity while maintaining weather resistance and preventing snow infiltration in climate zones where wind-driven snow presents a challenge. Documentation and quality verification during construction provide assurance that installed systems meet design intent. Photographic documentation of air gap installation at key stages—showing batten spacing, fastener patterns, and vent installations—creates a record proving compliance with specifications. Random field measurements of installed air gap depths verify consistency across the roof surface. These quality control measures prove especially valuable for large commercial or institutional projects where Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems cover extensive areas and minor installation deficiencies could multiply into significant performance compromises.
Conclusion
Air gap requirements in metal roofing deserve rigorous attention during design and installation phases, as these critical ventilation channels fundamentally influence long-term system performance, durability, and energy efficiency. Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems benefit from optimized air gaps that manage moisture, control thermal transfer, and extend service life through reduced panel operating temperatures. Climate-specific designs, proper material selections, and quality installation practices ensure your metal roofing investment delivers decades of reliable, cost-effective performance.
Cooperate with Xi'an Huafeng Construction Engineering Co., Ltd.
Xi'an Huafeng Construction Engineering Co., Ltd., established in 2018, specializes in comprehensive Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems with complete design, manufacturing, and installation capabilities. As a recognized high-tech enterprise in Shaanxi Province holding first-level curtain wall and third-level steel structure qualifications, Huafeng operates extensive production facilities including a 200,000-square-meter raw material plant in Anhui and processing facilities in Hangzhou and Xi'an. Our seven color coating production lines and advanced equipment deliver precision-manufactured panels in aluminum-magnesium-manganese, galvalume, stainless steel, titanium-zinc, and copper with PVDF coatings ensuring 30-year performance. ISO9001, ISO14000:14001, and SGS certifications validate our quality systems, while over 20 registered patents demonstrate our technical innovation. As a China Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems factory, China Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems supplier, and China Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems manufacturer offering China Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems wholesale, we provide Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems for sale at competitive Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems price points. Our High Quality Metal Standing Seam Roofing Systems have been installed at prestigious projects including Xiongan Station, Xi'an International Convention Center, and multiple airports and cultural facilities. Contact huafeng@hfmetalroof.com to discuss your project requirements and discover how our one-stop solution—from design optimization through precision manufacturing to professional installation—creates exceptional value for your metal roofing investment.
References
1. Miller, W.A., et al. "Field Testing of Metal Roofs with Above-Sheathing Ventilation in Hot-Humid Climates." Oak Ridge National Laboratory Building Technologies Research and Integration Center.
2. Lstiburek, J. "Ventilating Metal Roofs." Building Science Corporation Technical Building Bulletins.
3. International Residential Code. "Section R806: Roof Ventilation Requirements and Air Space Specifications." International Code Council.
4. Pfeiffer, P. "High-Performance Roof Assemblies for Hot-Humid Climates: Metal Roofing and Ventilation Strategies." Building Science Press.