Aluminum alloy 3004 is a versatile and widely used material in various industries, known for its exceptional combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and formability. This alloy belongs to the 3000 series of aluminum alloys, which are characterized by manganese as the primary alloying element. In this blog post, we'll delve into the unique properties of aluminum alloy 3004, exploring its chemical composition, mechanical characteristics, and applications. Whether you're involved in manufacturing, construction, or engineering, understanding the properties of this remarkable alloy can help you make informed decisions about material selection for your projects.
Chemical Composition and Microstructure of Aluminum Alloy 3004
Essential Elements in Aluminum Alloy 3004
Aluminum alloy 3004 is primarily composed of aluminum, with key alloying elements including manganese (Mn), magnesium (Mg), and iron (Fe). Manganese, typically ranging from 0.8-1.3%, enhances the alloy's strength and improves its resistance to corrosion. Magnesium, also present in similar amounts, contributes to both the strength and the overall workability of the alloy. Iron, typically up to 0.7%, helps stabilize the grain structure and further boosts the strength of the material. The careful selection of these elements ensures the alloy's performance across a wide range of applications.

Impact of Alloying Elements on Properties
The alloying elements in aluminum alloy 3004 have a profound impact on its mechanical properties. Manganese is primarily responsible for improving the alloy's strength while enhancing its resistance to corrosion, particularly in industrial environments. Magnesium contributes to the alloy's improved workability and further strengthens the material, making it more durable. Iron plays a key role in refining the microstructure, which results in improved strength and better control of the grain structure. Together, these elements provide a well-rounded balance of strength, formability, and corrosion resistance for the alloy.
Microstructural Features
The microstructure of aluminum alloy 3004 plays a vital role in its mechanical properties. It consists of a solid solution of the alloying elements within the aluminum matrix, which enhances its overall strength and durability. Intermetallic compounds, such as Al6Mn and Al3Mg2, are present and contribute significantly to the alloy's hardness and strength. The size and distribution of these compounds are critical in determining the material's properties, particularly its ability to resist corrosion and withstand stress. These features enable aluminum alloy 3004 to perform exceptionally well in a variety of demanding applications.
Mechanical Properties and Performance Characteristics
Tensile Strength and Yield Strength
Aluminum alloy 3004 demonstrates strong mechanical properties, which are crucial for a variety of industrial applications. In its annealed (O temper) state, the alloy typically offers a tensile strength of 180-200 MPa and a yield strength of 75-90 MPa. When the alloy undergoes work-hardening (H tempers), its mechanical properties improve significantly. In this hardened condition, the tensile strength can reach up to 285 MPa, and yield strength can go as high as 250 MPa, making it highly suitable for structural components requiring greater load-bearing capacity.
Ductility and Formability
One of the key advantages of aluminum alloy 3004 is its excellent ductility, particularly when in the annealed (O temper) state. The alloy exhibits elongation values ranging from 15% to 25%, which indicates its capacity to undergo significant deformation without fracturing. This high ductility allows the material to be easily formed into complex shapes through processes like deep drawing and stretch forming, making it ideal for industries such as automotive and packaging, where intricate shapes and thin-walled components are common.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Aluminum alloy 3004 is known for its exceptional resistance to corrosion, especially in outdoor and atmospheric environments. The alloy's composition, including the presence of manganese and magnesium, facilitates the formation of a stable, protective oxide layer on its surface. This oxide layer effectively shields the alloy from corrosion caused by exposure to moisture, chemicals, and air. As a result, aluminum alloy 3004 is well-suited for applications in environments prone to corrosion, such as in architectural panels, roofing, and outdoor equipment.
Applications and Industry Uses of Aluminum Alloy 3004
Building and Construction
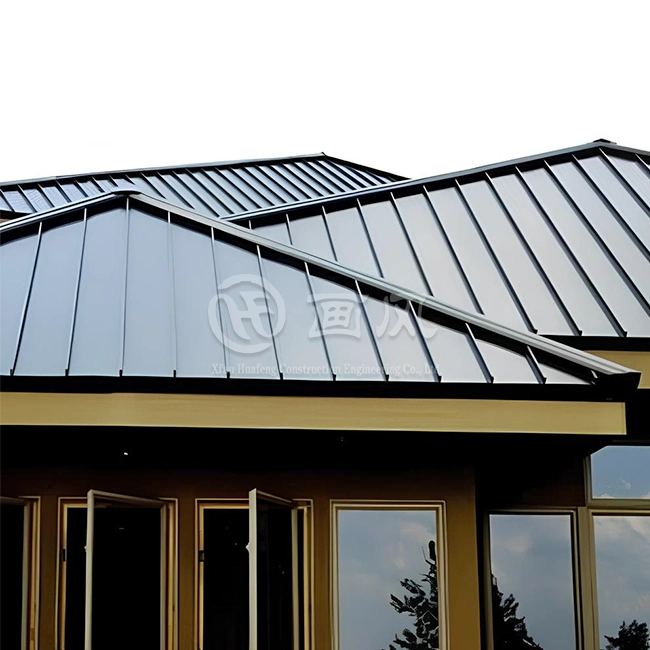
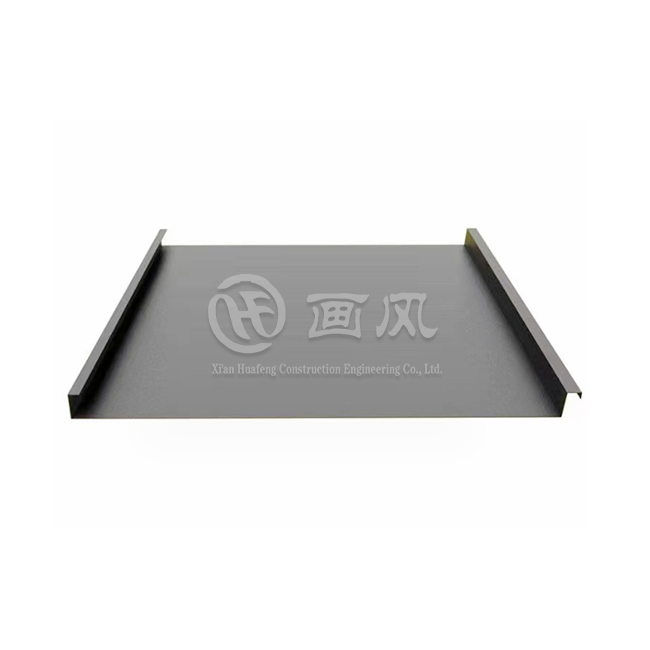
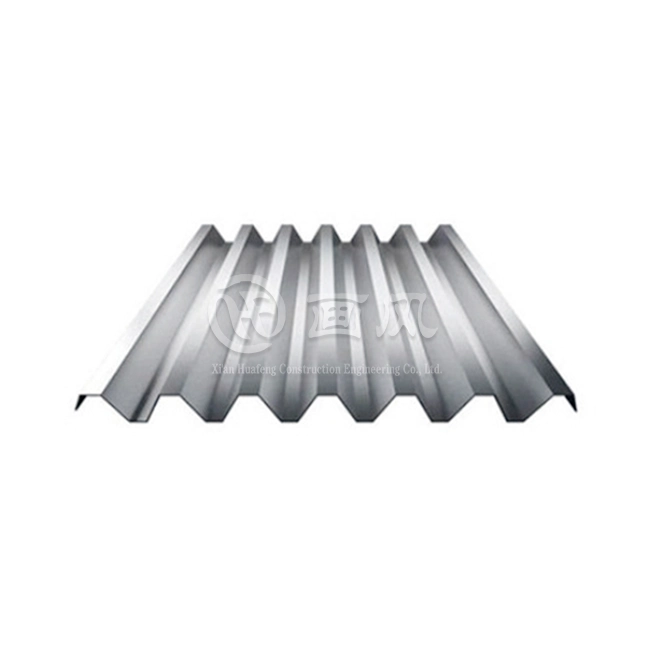
Aluminum alloy 3004 is highly valued in the building and construction industry for its versatility and performance in a wide range of applications. Its strength, durability, and resistance to weathering make it an ideal material for roofing and siding. The alloy is commonly used in standing seam metal roofs, which require materials that can withstand harsh weather conditions without losing structural integrity. Additionally, aluminum alloy 3004 is frequently used in gutters, downspouts, and cladding, where its aesthetic appeal and long-lasting finish contribute to both functionality and visual appeal in architectural designs.
Packaging and Consumer Goods
Aluminum alloy 3004 plays a pivotal role in the packaging and consumer goods industries, particularly for food and beverage packaging. Its excellent formability allows manufacturers to produce intricate shapes like beverage cans and food containers. The alloy's corrosion resistance ensures that packaged products remain safe and protected from external elements, extending their shelf life. Moreover, as an environmentally friendly material, aluminum alloy 3004 is highly recyclable, making it a key choice in sustainable packaging solutions. Its ability to preserve product quality while being reusable makes it an essential material in modern packaging.
Transportation and Automotive
In the transportation and automotive industries, aluminum alloy 3004 is favored for its lightweight yet durable characteristics. Its strength and corrosion resistance make it ideal for components like vehicle body panels, fuel tanks, and heat exchangers. The alloy's ability to be easily formed into complex shapes helps manufacturers create intricate automotive parts that improve vehicle aerodynamics and performance. Additionally, the alloy's light weight contributes to enhanced fuel efficiency by reducing the overall weight of vehicles. As a result, aluminum alloy 3004 plays a critical role in advancing both the performance and environmental sustainability of modern transportation systems.
Conclusion
Aluminum alloy 3004 stands out as a versatile material with a unique combination of properties that make it invaluable across various industries. Its balanced chemical composition, excellent mechanical properties, and superior corrosion resistance contribute to its widespread adoption in construction, packaging, and transportation sectors. As industries continue to seek lightweight, durable, and sustainable materials, aluminum alloy 3004 remains a compelling choice for diverse applications. If you want to get more information about this product, you can contact us at huafeng@hfmetalroof.com
References
1. Kaufman, J. G. (2000). Introduction to Aluminum Alloys and Tempers. ASM International.
2. Davis, J. R.(Ed.). (1993). Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys. ASM International.
3. Hatch, J. E. (Ed.). (1984). Aluminum: Properties and Physical Metallurgy. ASM International.
4. Sanders, R. E. (2001). Technology Innovation in Aluminum Products. JOM, 53(2), 21-25.
5. Polmear, I. J. (2006). Light Alloys: From Traditional Alloys to Nanocrystals. Butterworth-Heinemann.
6. Mondolfo, L. F. (1976). Aluminum Alloys: Structure and Properties. Butterworths.